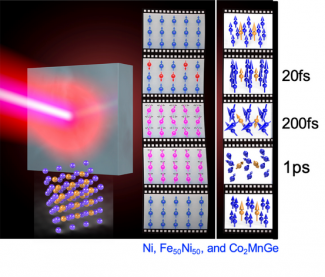
Figure: Direct light-induced spin manipulation on few-femtosecond timescales. High harmonic based ARPES combined with element-specific magneto-optic probes uncovered a fundamentally new understanding of how magnets respond to light. In Ni, a new super-excited magnetic state is created, launching a magnetic phase transition within <20 fs. In Co2MnGe and Fe50Ni50, spin polarization can be directly transferred from one element to another in the process of absorbing a photon. This is the fastest route demonstrated for manipulating magnetic materials to date.
Capturing the fastest spin dynamics in magnetic materials
Magnetism has been the subject of scientific inquiry for more than 2000 years. However, it is still an incompletely understood phenomenon. The fundamental length and time scales for magnetic phenomena range from Å (exchange lengths) and sub-femtoseconds (exchange splitting) on up. Furthermore, a detailed understanding of nanoscale magnetism is critical in the 21st century with dramatic increases in data usage and the the critical need for faster, energy-efficient nanodevices. However, a comprehensive microscopic model of how spins, electrons, photons and phonons interact does not yet exist. This understanding is fundamentally constrained in large part by a limited ability to directly observe magnetism on all relevant time and length scales - and tools for addressing these questions have only recently become available.
Ultrafast X-ray pulses make it possible to probe element-specific spin dynamics in multi-component magnetic systems, providing rich new information not accessible using visible light. Our recent research has shown that extreme ultraviolet (EUV) high harmonic beams are ideal for capturing the fastest spin dynamics in magnetic materials.[1-24] By combining HHG sources with new spectroscopic and imaging techniques, we have made a series of new discoveries. In exciting recent work, we showed that light can manipulate spins in many materials on few-femtosecond to attosecond timescales. This could not be observed previously, because many spectroscopic probes average over all excitations and sample depths - and are simply not sensitive to the unique laser-induced spin states present in the material. Key to uncovering this new understanding was a suite of correlated high harmonic based spectroscopies (time- and angle-resolved photoemission (EUV ARPES), combined with element-specific magneto-optic probes (e.g., EUV MOKE, XMCD), that make it possible to detect unique spin excitations present in the material, as illustrated in the Figure. For example, direct (near-instantaneous) light-induced spin transfer can occur between two elements in magnetic materials, during the light pulse itself––achieving the fastest manipulation of spins to date.
Looking to the future, it is now possible to extend these new spectroscopy and imaging measurements to the L absorption edges of magnetic media in the soft x-ray region of the spectrum. Recent advances in generating bright, coherent, x-rays from femtosecond lasers in the keV region of the spectrum make this feasible for the first time. Imaging of buried magnetic structures, domain interactions, strongly coupled nano layers, and spin dynamics will all be accessible with femtosecond time and nanometer spatial resolution.
Related Publications
-
P. Tengdin, C. Gentry, A. Blonsky, D. Zusin, M. Gerrity, L. Hellbrück, J. Shaw, Y. Kvashnin, E. K. Delczeg-Czirjak, M. Arora, H. Nembach, T. J. Silva, S. Mathias, M. Aeschlimann, H. C. Kapteyn, D. Thonig, K. Koumpouras, O. Eriksson, M. Murnane, “Direct light-induced spin transfer between different elements in a spintronic Heusler material via femtosecond laser excitation,” Science Advances 6, eaaz1100, (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz1100
-
M. Hofherr, S. Häuser, J. K. Dewhurst, P. Tengdin, S. Sakshath, H. T. Nembach, S. T. Weber, J. M. Shaw, T. J. Silva, H. C. Kapteyn, M. Cinchetti, B. Rethfeld, M. M. Murnane, D. Steil, B. Stadtmüller, S. Sharma, M. Aeschlimann, S. Mathias, “Ultrafast optically induced spin transfer in ferromagnetic alloys,” Science Advances 6, eaay8717 (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay8717
-
X. Shi, C.-T. Liao, Z. Tao, E. Cating-Subramanian, M. M. Murnane, C. Hernández-García, H. C. Kapteyn, “Attosecond light science and its application for probing quantum materials, Invited paper, JPhys Photonics/JPhys B Attosecond focus issue 53, 184008 (2020). DOI: 10.1088/1361-6455/aba2fb
-
R. Schoenlein, T. Elsaesser, K. Holldack, Z. Huang, H. Kapteyn, M. Murnane, M. Woerner, “Recent advances in ultrafast X-ray sources,” Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 377: 20180384 (2019). DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2018.0384
-
P. Tengdin, W. You, C. Chen, X. Shi, D. Zusin, Y. Zhang, C. Gentry, A. Blonsky, M. Keller, P. Oppeneer, H. Kapteyn, Z. Tao, M. Murnane, “Critical behavior within 20fs drives the out-of-equilibrium laser-induced magnetic phase transition in nickel,” Science Advances 4, 9744 (2018). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aap9744
-
W. You, P. Tengdin, C. Chen, X. Shi, D. Zusin, Y. Zhang, C. Gentry, A. Blonsky, M. Keller, P. M. Oppeneer, H. Kapteyn, Z. Tao, M. Murnane, “Revealing the nature of the ultrafast magnetic phase transition in Ni by correlating extreme ultraviolet magneto-optic and photoemission spectroscopies,” Physical Review Letters 121, 077204 (2018). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.077204
-
M. Hofherr, S. Moretti, J. Shim, S. Häuser, N.Y. Safonova, M. Stiehl, A. Ali, S. Sakshath, J.W. Kim, D.H. Kim, H.J. Kim, J.I. Hong, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, M. Cinchetti, D. Steil, S. Mathias, B. Stadtmüller, M. Albrecht, D.E. Kim, U. Nowak, M. Aeschlimann, “Induced vs. intrinsic magnetic moments in ultrafast magnetization dynamics,” Physical Review B 98, 174419 (2018). DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.98.174419. Also selected as an Editor’s Suggestion.
-
D. Zusin, P. Tengdin, M. Gopalakrishnan, C. Gentry, A. Blonsky, M. Gerrity, D. Legut, J. Shaw, H. Nembach, T. Silva, P. Oppeneer, H. Kapteyn, M. Murnane, “Direct measurement of the static and transient magneto-optical permittivity of cobalt across the entire M-edge in a reflection geometry by use of polarization scanning,” Physical Review B 97, 024433 (2018). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.97.024433
-
S. Eich, M. Plötzing, M. Rollinger, S. Emmerich, R. Adam, C. Chen, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, L. Plucinski, D. Steil, B. Stadtmüller, M. Cinchetti, M. Aeschlimann, C. M. Schneider, S. Mathias, “Band-structure evolution during the ultrafast ferromagnetic-paramagnetic phase transition in cobalt,” Science Advances 3, e1602094 (2017). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1602094
-
C. Chen, Z. Tao, A. Carr, P. Matyba, T. Szilvási, S. Emmerich, M. Piecuch, , M. Keller, D. Zusin, S. Eich, M. Rollinger, W. You, S. Mathias, U. Thumm, M. Mavrikakis, M. Aeschlimann, P. Oppeneer, H. Kapteyn, M. Murnane, “Distinguishing attosecond electron-electron scattering and screening in transition metals,” PNAS 114 (27) E5300–E5307 (2017). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1706466114
-
C. A. Mancuso, K. M. Dorney, D. D. Hickstein, J. L. Chaloupka, X-M. Tong, J. L. Ellis, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, “Observation of ionization enhancement in two-color circularly polarized laser fields,” Physical Review A 96, 023402 (2017). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.96.023402
-
E. Turgut, D. Zusin, D. Legut, , K. Carva, R. Knut, J. M. Shaw, C. Chen, Z. Tao, H. T. Nembach, T. Silva, S. Mathias, M. Aeschlimann, P. M. Oppeneer, H.C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, P. Grychtol, “Stoner vs Heisenberg: Ultrafast exchange reduction and magnon generation during laser-induced demagnetization,” Physical Review B 94, 220408(R) (2016). Also selected as Editor’s Suggestion. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.94.220408
-
S. Mathias, S. Eich, J. Urbancic, S. Michael, A.V. Carr, S. Emmerich, A. Stange, T. Popmintchev, T. Rohwer, M. Wiesenmayer, A. Ruffing, S. Jakobs, S. Hellmann, P. Matyba, C. Chen, L. Kipp, M. Bauer, H. C. Kapteyn, H. C. Schneider, K. Rossnagel, M. M. Murnane, M. Aeschlimann, “Self-amplified photo-induced gap quenching in a correlated electron material,” Nature Communications 7, 12902 (2016). DOI:10.1038/ncomms12902
-
O. Kfir, P. Grychtol, E. Turgut, R. Knut, D. Zusin, A. Fleischer, E. Bordo, T. Fan, D. Popmintchev, T. Popmintchev, H. Kapteyn, M. Murnane, O. Cohen, “Helicity-selective phase-matching and quasi-phase matching of circularly polarized high-order harmonics: towards chiral attosecond pulses,” invited paper, Journal of Physics B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 49 (2016) 123501. DOI: 10.1088/0953-4075/49/12/123501
-
K. M. Hoogeboom-Pot, E. Turgut, J. N. Hernandez-Charpak, J. M. Shaw, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, D. Nardi, “Nondestructive measurement of the evolution of layer-specific mechanical properties in sub-10 nm bilayer films,” Nano Letters 16 (8), 4773–4778 (2016). DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00606
-
O. Kfir, P. Grychtol, E. Turgut, R. Knut, D. Zusin, D. Popmintchev, T. Popmintchev, H. Nembach, J. M. Shaw, A. Fleischer, H. Kapteyn, M. Murnane, O. Cohen, “Generation of bright phase-matched circularly-polarized extreme ultraviolet high harmonics,” Nature Photonics 9, 99–105 (2015). DOI: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.293
-
C. Weier, R. Adam, D. Rudolf, R. Frömter, P. Grychtol, G. Winkler, A. Kobs, H. P. Oepen, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, C. M. Schneider, “Femtosecond-laser-induced modifications in Co/Pt multilayers studied with tabletop resonant magnetic scattering,” Europhysics Letters 109, 17001 (2015). DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/109/17001
-
T. Fan, P. Gychtol, R. Knut, C. Hernández-García, D. D. Hickstein, D. Zusin, C. Gentry, F. J. Dollar, C. A. Mancuso, C. W. Hogle, O. Kfir, D. Legut, K. Carva, J. L. Ellis, K. M. Dorney, C. Chen, O. G. Shpyrko, E. E. Fullerton, O. Cohen, P. M. Oppeneer, D. B. Milošević, A. Becker, A. Jarón-Becker, T. Popmintchev, M. M. Murnane, H. C. Kapteyn, “Bright Circularly Polarized Soft X-Ray High Harmonics for X-Ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism,” PNAS 112 (46) 14206–14211 (2015). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1519666112
-
S. Mathias, C. La-o-Vorakiat, J. M. Shaw, E. Turgut, P. Grychtol, R. Adam, D. Rudolf, H. T. Nembach, T. J. Silva, M. Aeschlimann, C. M. Schneider, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, “Ultrafast element-specific magnetization dynamics of complex magnetic materials on a table-top,” invited review paper, Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena 189, 164 (2013). DOI:10.1016/j.elspec.2012.11.013
-
E. Turgut, C. La-o-Vorakiat, J. M. Shaw, P. Grychtol, H. T. Nembach, D. Rudolf, R. Adam, M. Aeschlimann, C. M. Schneider, T. J. Silva, M. M. Murnane, H. C. Kapteyn, S. Mathias, “Controlling the competition between optically induced ultrafast spin-flip scattering and spin transport in magnetic multilayers,” Physical Review Letters 110, 197201 (2013). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.197201
-
D. Rudolf, C. La-O-Vorakiat, M. Battiato, R. Adam, J. M. Shaw, E. Turgut, P. Maldonado, S. Mathias, P. Grychtol, H. T. Nembach, T. J. Silva, M. Aeschlimann, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, C. M. Schneider, P. M. Oppeneer, “Ultrafast magnetization enhancement in metallic multilayers driven by superdiffusive spin current,” Nature Communications 3, 1037 (2012). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2029
-
S. Mathias, C. La-O-Vorakiat, P. Grychtol, Patrick G., Emrah T., J. M. Shaw, R. Adam, H. T. Nembach, M. E. Siemens, S. Eich, C. M. Schneider, T. J. Silva, M. Aeschlimann, M. M. Murnane, and H. C. Kapteyn, “Probing the timescale of the exchange interaction in a ferromagnetic alloy,” PNAS 109, 4792 (2012). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201371109
-
C. La-O-Vorakiat, E. Turgut, C. A. Teale, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, S. Mathias, M. Aeschlimann, C. M. Schneider, J. M. Shaw, H. Nembach, T. J. Silva, “Ultrafast demagnetization measurements using extreme ultraviolet light: Comparison of electronic and magnetic contributions,” Physical Review X 2, 011005 (2012). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.2.011005
-
C. La-O-Vorakiat, M. Siemens, M. M. Murnane, H. C. Kapteyn, S. Mathias, M. Aeschlimann, P. Grychtol, R. Adam, C. M. Schneider, J. M. Shaw, H. Nembach, T. J. Silva, “Ultrafast demagnetization dynamics at the M edges of magnetic elements observed using a tabletop high-harmonic soft X-ray source,” Physical Review Letters 103, 257402 (2009). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.257402